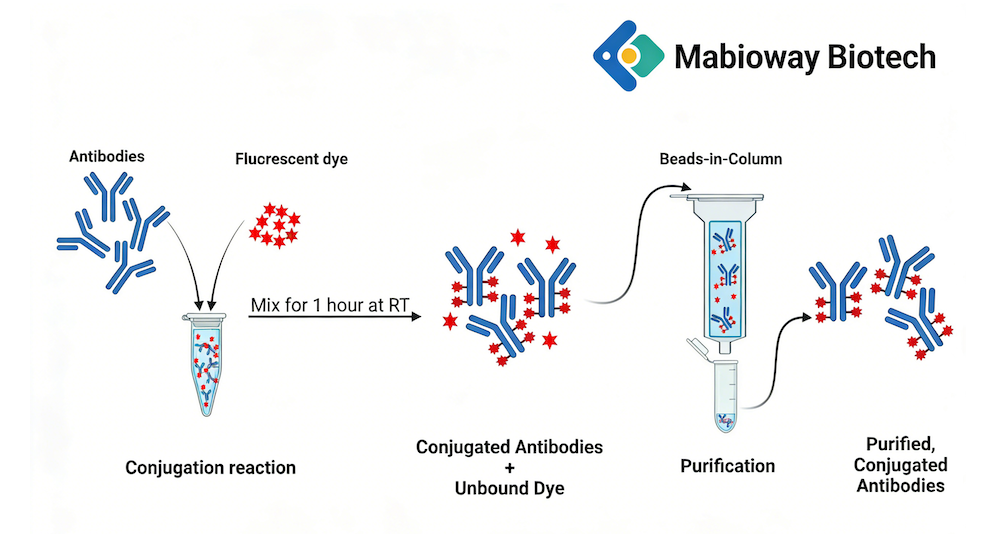
Cat. No.
MABL-2142
Application
fluorescence microscopy, in vitro, in vivo, IP, WB, ELISA, FC, IHC
Isotype
Engineer antibody
Species Reactivity
Bovine, Pig, Sheep, Human, Rhesus Monkey
Clone No.
83-14
From
Recombinant Antibody
Specificity
This antibody is specific for the extracellular domain of the human insulin receptor (HIR). Specifically, it recognizes amino acids 469 - 592 (exons 7 and 8) of the insulin receptor alpha subunit. Low to moderate cross-reaction with bovine IR was observed. This antibody also binds to the Rhesus monkey, pig, and sheep IR.
Alternative Names
CD220; Insulin Receptor alpha; HHF5; IR; HIR
UniProt
P06213
Immunogen
The original antibody was generated by immunizing Balb/c mice with IM-9 lymphocytes followed by purified human insulin receptor.
Application Notes
The original format of this antibody (mouse IgG2a) was generated, and its binding to the HIR was characterized via ELISA, Western blot, and immunoprecipitation assays. Its epitope was characterized through competition/inhibitory experiments (Soos et al., 1986; PMID: 2427071). This antibody was used to study the internalization of the HIR (Paccaud et al., 1992; PMID: 1618809), demonstrating that it facilitated constitutive internalization of the HIR via clathrin-coated pits, independent of receptor kinase activation or autophosphorylation. This process reflected the natural homeostasis of HIR on the cell surface and was mediated by the receptor's interaction with the clathrin machinery. The Fab format of the antibody was created and exhibited the same internalization rates as the full antibody, confirming that the process was not influenced by inter- or intramolecular cross-linking (Paccaud et al., 1992; PMID: 1618809). In an in vitro setting, a radiolabeled 125I version of this antibody strongly bound the Rhesus monkey brain capillary insulin receptor in an IHC assay. It demonstrated an ED50 of 0.09 µg/ml (0.60 nM) toward isolated human brain capillaries from autopsy, with a calculated KD of 0.45 ± 0.10 nM. In vivo, the 125I-labeled version crossed the blood-brain barrier (BBB) rapidly via receptor-mediated transcytosis, with approximately 40% of its brain distribution volume attributed to postvascular compartments, as shown by capillary depletion methods. Pharmacokinetic analysis revealed an initial rapid clearance phase within 15 minutes of intravenous injection, followed by stable plasma concentrations with a mean residence time of 7–16 hours. This enabled delivery of 3–4% of the injected dose to the brain, with preferential uptake in gray matter (Pardridge et al., 1995; PMID: 7667183). This antibody was further studied in in vitro experiments with hCMEC/D3 cells, a human brain endothelial cell model. A fluorescently labeled version was used to confirm its functionality via flow cytometry, demonstrating successful binding to insulin receptor-expressing cells. To explore its potential for drug delivery, the antibody was conjugated to PDMS-b-PMOXA polymersomes, and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) validated the conjugation efficiency. Cellular uptake and intracellular localization of the conjugated and free antibody were visualized through confocal laser scanning microscopy. Specificity for receptor-mediated uptake was confirmed in a competitive inhibition assay, where excess free mAb blocked the polymersome uptake (Dieu et al., 2014; PMID: 7667183). This antibody was further studied in in vitro experiments with hCMEC/D3 cells, a human brain endothelial cell model. A fluorescently labeled version was used to confirm its functionality via flow cytometry, demonstrating successful binding to insulin receptor-expressing cells. To explore its potential for drug delivery, the antibody was conjugated to PDMS-b-PMOXA polymersomes, and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) validated the conjugation efficiency. Cellular uptake and intracellular localization of the conjugated and free antibody were visualized through confocal laser scanning microscopy. Specificity for receptor-mediated uptake was confirmed in a competitive inhibition assay, where excess free mAb blocked the polymersome uptake (Dieu et al., 2014; PMID: 24929212). This antibody effectively bound multiple mutant human INSRs expressed on the cell surface of 3T3-L1 adipocytes (a mouse-derived cell line transfected with human mutant INSR constructs) in vitro. It induced receptor autophosphorylation, measured using an immunocapture assay with myc-tagged receptors, and selectively activated the Akt pathway, as shown by Western blotting for phospho-Akt. This activation drove insulin's metabolic effects while minimizing mitogenic ERK activation. The antibody also stimulated glucose uptake in cells expressing certain mutants (e.g., P193L, S323L, F382V, D707A), with responses sometimes exceeding those of insulin, as quantified in a glucose uptake assay. Its efficacy depended on receptor cross-linking rather than specific epitope recognition, as demonstrated across a series of in vitro assays (Brierley et al., 2018; PMID: 29700562). A humanized version of this antibody was generated and is available as a separate product (see Ab04886).
Antibody First Published
Soos et al. Monoclonal antibodies reacting with multiple epitopes on the human insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):199-208. PMID:2427071
Note on publication
The original publication describes the immunization of mice with IM-9 an purified human insulin receptor and the identification of the insulin receptor alpha extracellular domain epitope.
Size
100 μg Purified antibody.
Concentration
1 mg/ml.
Purification
Protein A affinity purified
Buffer
PBS with 0.02% Proclin 300.
Storage Recommendation
Store at 4⁰C for up to 3 months. For longer storage, aliquot and store at - 20⁰C.