Cat. No.
MAK-0004
Product Name
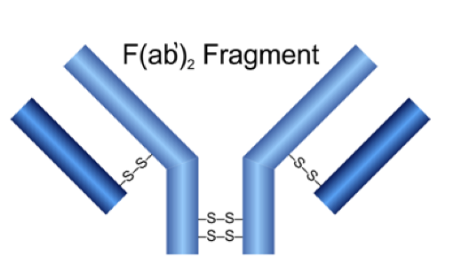
F(ab
Size
10 samples for 250ug-4mg IgG
Storage
4–8°C.
Principle
Immobilized Pepsin
Description
Mabioway F(ab
Features
• Ideal when sample size is limited—Use the micro kit for 25 to 250 μg IgG.• Enzyme-free digestion products—Immobilized Pepsin (beaded agarose resin) provides for control of the digestion reaction and complete removal of resulting antibody fragments from the proteolytic enzyme• Suitable for human and other species of IgG—the kit procedure is optimized for human, rabbit and mouse IgG. Pepsin-based digestion is effective for other species and subclasses of IgG, although the purification step requires that the antibody effectively binds to Protein A . (Note: for best results with mouse IgG1, use Part No. MAK-0006.)• Complete—kits include all reagents needed to prepare and purify antibody fragments• Fast— format greatly reduces sample processing time• Flexible—protocols are included for multiple species and IgG subclasses, as well as sample size and concentration.• Efficient—enhanced yield and sample purity
Contents
10 antibody samples, each containing 25 to 250 μg IgG• Immobilized Pepsin Agarose, 0.5 mL• F(ab
Additional Materials
• Incubator capable of maintaining 37°C• Microcentrifuge capable of 5000 × g• Variable speed centrifuge• 1.5mL microcentrifuge tubes• End-over-end mixer or tabletop rocker
Material Preparation
Phosphate-buffered Saline (PBS): Dissolve contents of a package in 1000mL of ultrapure water. For long-term storage, add 0.05% sodium azide and store at 4°C.
Procedure
A. Immobilized Pepsin Equilibration1. Gently swirl the Immobilized Pepsin vial to obtain an even suspension. Seat the spin column frit with an inverted 200μL pipette tip.2. Tplace 50μL of the 50% slurry (i.e., 25μL of settled resin) into the 1.5mL Microcentrifuge Tubes at 5000 × g for 1 minute and discard buffer.3. Wash resin with 130μL of Digestion Buffer. Centrifuge column at 5000 × g for 1 minute and discard buffer.B. IgG Sample Preparation1. Desalting Column and loosen cap. Place column in a collection tube.2. Centrifuge column at 1500 × g for 1 minute to remove storage solution. Place a mark on the side of the column where the compacted resin is slanted upward. Place column in centrifuge with the mark facing outward in all subsequent centrifugation steps.Note: Resin will appear compacted after centrifugation.3. Add 300µL of Digestion Buffer to column. Centrifuge at 1500 × g for 1 minute to remove buffer. Repeat this step three additional times, discarding buffer from the collection tube.4. Place column in a new collection tube, apply 125µL of sample to the center of the compacted resin bed.5. centrifuge at 1500 × g for 2 minutes to collect the sample. Discard the column after use.6. If IgG sample is 0.2-2mg/mL (i.e., 25-250µg), no further preparation is necessary. If sample volume is less than 125µL, add Digestion Buffer to a final volume of 125µL.C. Fragment Generation1. Add 125µL of the prepared IgG sample to the column containing the equilibrated Immobilized Pepsin (Section A). Briefly vortex to mix.2. Incubate digestion reaction for 2 hours for rabbit or human IgG or 3 hours for mouse IgG with an end-over-end mixer or tabletop rocker at 37°C. Maintain constant mixing of resin during incubation.3. Centrifuge column at 5000 × g for 1 minute to separate digest from the Immobilized Pepsin.4. Wash resin with 130µL of PBS. Place column into a new tube and centrifuge at 5000 × g for 1 minute. Repeat this step once.5. Add both wash fractions to the digested antibody. Total sample volume should be 385µL. Discard the Immobilized Pepsin.Note: For best results, evaluate the digest and wash fraction via SDS-PAGE to assess digestion completion. Protein A purification is only required to remove undigested IgG. F(ab´)2 and degraded Fc do not bind to Protein A . The resulting F(ab´)2 in non-reducing SDS-PAGE derived from human and mouse IgG will migrate with an apparent molecular weight of ~110kDa. Rabbit F(ab´)2 will migrate with a lower apparent molecular weight of ~88kDa. D. F(ab´)2 Purification1. Equilibrate the Protein A Column, PBS and IgG Elution Buffer to room temperature. Set centrifuge to 1000 × g.2. Place column in a collection tube and centrifuge for 1 minute to remove storage solution (contains 0.02% sodium azide). Discard the flow-through.3. To equilibrate column, add 400µL of PBS and briefly mix. Centrifuge for 1 minute and discard the flow-through. Repeat this step once.4. Apply 25-500µL sample to column and cap the top tightly. Resuspend the resin and sample by inversion. Incubate at room temperature with end-over-end mixing for 10 minutes.5. Place column in a new collection tube and centrifuge for 1 minute. Save the flow-through as this fraction contains F(ab´)2 and Fc fragments that are too small to bind to Protein A .6. For optimal recovery, wash column with 200µL of PBS. Centrifuge for 1 minute and collect flow-through. Repeat and combine wash fractions with the F(ab´)2 fraction from Step 5.7. Measure protein concentration using the BCA Protein A ssay or by measuring the absorbance at 280nm. Use an estimated extinction coefficient of 1.4. Assuming complete IgG digestion, F(ab´)2 yields may vary from 50 to 70%, depending on the amount of starting antibody and the Protein A ssays used.8. If desired, perform dialysis (50K MWCO), gel filtration or ion-exchange chromatography to remove the Fc fragments that are too small to bind to Protein A .E. Regeneration of the Immobilized Protein A Column1. Apply 400µL of IgG Elution Buffer to the Protein A Column. Centrifuge for 1 minute. Repeat this step two times to obtain three fractions, which will contain undigested IgG. To save the undigested IgG, add 40µL of a neutralization buffer (e.g., 1M phosphate or 1M Tris at pH 8-9) to each elution fraction.2. Add 400µL of IgG Elution Buffer to the column and centrifuge for 1 minute. Discard flow-through and repeat.3. Add 400µL of PBS to the column and centrifuge for 1 minute. Discard flow-through and repeat two times.4. For storage, add 400µL of 0.02% sodium azide in PBS to column. replace top and bottom caps. Store column upright at 4°C. Columns can be regenerated at least 10 times without significant loss of binding capacity.
Trouble shooting
Problem 1: Low amounts of F(ab´)2 produced as determined by non-reducing SDS-PAGE1)IgG sample was not in Digestion BufferDialyze or buffer exchange IgG into DigestionBuffer, or decrease the Digestion Buffer pH to 3-4.3Note: Decreasing the pH might increase the F(ab´)2 amount produced but can reduce its immunoreactivity]2)Sample loading buffer contains reducing reagentUse SDS loading buffer that does not contain β-mercaptoethanol, DTT or TCEP3)Resin was not equilibrated in Digestion Buffer before adding IgGWash resin with 0.5mL of Digestion Buffer before adding IgG sample4)Sample is goat or mouse IgG1Reduce IgG concentration and increase digestion time to 8 hours5)Some mouse IgG1 are resistant to pepsin cleavageUse the IgG1 Fab and F(ab´)2 Preparation kit (Product No. 44980 or 44680)6)Sample contains protein other than IgG (e.g., BSA), which can increase digestion timeRemove BSA with the Antibody Clean-up Kit (Product No. 44600)Problem 2: F(ab´)2 has low immunoreactivity1)Sample digested for too long Reduce digestion time; do not exceed 8 hours2)The low pH of Digestion Buffer decreased F(ab´)2 activityUse the IgG1 Fab and F(ab´)2 Preparation KitProblem 3: Low F(ab´)2 recoveryIncomplete washing of the pepsin resin Two 130µL washes of PBS are required for maximum recoveryProblem 4: A portion of undigested IgG does not bind to Protein A 1)Sample is goat or mouse IgG1 a. Goat IgG binds weakly to Protein A , so try an alternative purification method such as ion-exchangeb. Dilute sample in Protein A Binding Buffer before adding to the Protein A Column
![]() MAK-0004-F(ab')2 Micro Preparation Kit.pdf
MAK-0004-F(ab')2 Micro Preparation Kit.pdf